WebSocket
Reference
26. WebSocket Support
This part of the reference documentation covers Spring Framework’s support for WebSocket-style messaging in web applications including use of STOMP as an application level WebSocket sub-protocol. Section 26.1, “Introduction” establishes a frame of m
docs.spring.io
[Spring Boot] WebSocket과 채팅 (3) - STOMP
[Spring Boot] WebSocket과 채팅 (3) - STOMP
[Spring Boot] WebSocket과 채팅 (2) - SockJS [Spring Boot] WebSocket과 채팅 (1) 일전에 WebSocket(웹소켓)과 SockJS를 사용해 Spring 프레임워크 환경에서 간단한 하나의 채팅방을 구현해본 적이 있다. [Sprin..
dev-gorany.tistory.com
Spring websocket chatting server(1) - basic websocket server
웹소켓(websocket)으로 채팅서버 만들기
웹소켓(websocket)으로 채팅서버 만들기
daddyprogrammer.org
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rvss-_t6gzg
26.1 Introduction
💡 A proper introduction to the WebSocket protocol is beyond the scope of this document. At a minimum however it’s important to understand that HTTP is used only for the initial handshake, which relies on a mechanism built into HTTP to request a protocol upgrade (or in this case a protocol switch) to which the server can respond with HTTP status 101 (switching protocols) if it agrees handshaking. Assuming the handshake succeeds the TCP socket underlying the HTTP upgrade request remains open and both client and server can use it to send messages to each other.
26.1.2 A Messaging Architecture
💡 By contrast a WebSocket application may use a single URL only for the initial HTTP handshake. All messages thereafter share and flow on the same TCP connection.
26.1.3 Sub-Protocol Support in WebSocket
💡 Unlike HTTP, which is an application-level protocol, in the WebSocket protocol there is simply not enough information in an incoming message for a framework or container to know how to route it or process it. Therefore WebSocket is arguably too low level for anything but a very trivial application. For this reason the WebSocket RFC defines the use of sub-protocols. The use of a sub-protocol is not required, but even if not used, applications will still need to choose a message format that both the client and server can understand. STOMP-a standard messaging protocol is widely supported and well suited for use over WebSocket and over the web.
26.1.4 Should I use WebSocket?
💡 It is the combination of both low latency and high frequency of messages that can make the use of the WebSocket protocol critical. The Spring Framework allows @Controller and @RestControllerclasses to have both HTTP request handling and WebSocket message handling methods.
26.2 WebSocket API
WebSocketHandler
import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketHandler;
import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketSession;
import org.springframework.web.socket.TextMessage;
*//implement WebSocketHandler or more likely extending either
//TextWebSocketHandler or BinaryWebSocketHandler*
public class MyHandler extends TextWebSocketHandler {
@Override
public void handleTextMessage(WebSocketSession session, TextMessage message) {
// ...
}
}
WebSocketConfig
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.EnableWebSocket;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketHandlerRegistry;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocket
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) {
*//mapping the WebSocket handler to a specific URL*
registry.addHandler(myHandler(), "/myHandler");
}
@Bean
public WebSocketHandler myHandler() {
return new MyHandler();
}
}
WebSocket Handshake
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocket
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addHandler(new MyHandler(), "/myHandler")
.addInterceptors(new HttpSessionHandshakeInterceptor());
}
}
💡 The easiest way to customize the initial HTTP WebSocket handshake request is through a HandshakeInterceptor, which exposes "before" and "after" the handshake methods. Such an interceptor can be used to preclude the handshake or to make any attributes available to the WebSocketSession.
26.2.6 Configuring allowed origins
💡 The default behavior for WebSocket and SockJS is to accept only same origin requests. It is also possible to allow all or a specified list of origins. The 3 possible behaviors are: 1) Allow only same origin requests (default) 2) Allow a specified list of origins: each provided allowed origin must start with http:// or https:// 3) Allow all origins: to enable this mode, you should provide ’’ as the allowed origin value.*
26.3 SockJS Fallback
26.3.2 Enable SockJS
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocket
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addHandler(myHandler(), "/myHandler").withSockJS();
}
@Bean
public WebSocketHandler myHandler() {
return new MyHandler();
}
}
26.3.6 SockJS and CORS
💡 If you allow cross-origin requests the SockJS protocol uses CORS for cross-domain support in the XHR streaming and polling transports. Therefore CORS headers are added automatically unless the presence of CORS headers in the response is detected.
26.4 STOMP
💡 The WebSocket protocol defines two types of messages, text and binary, but their content is undefined. The use of a sub-protocol is optional but either way client and server will need to agree on some protocol that defines message content. STOMP can be used over any reliable 2-way streaming network protocol such as TCP and WebSocket. Although STOMP is a text-oriented protocol, the payload of messages can be either text or binary*.*
STOMP Protocol)
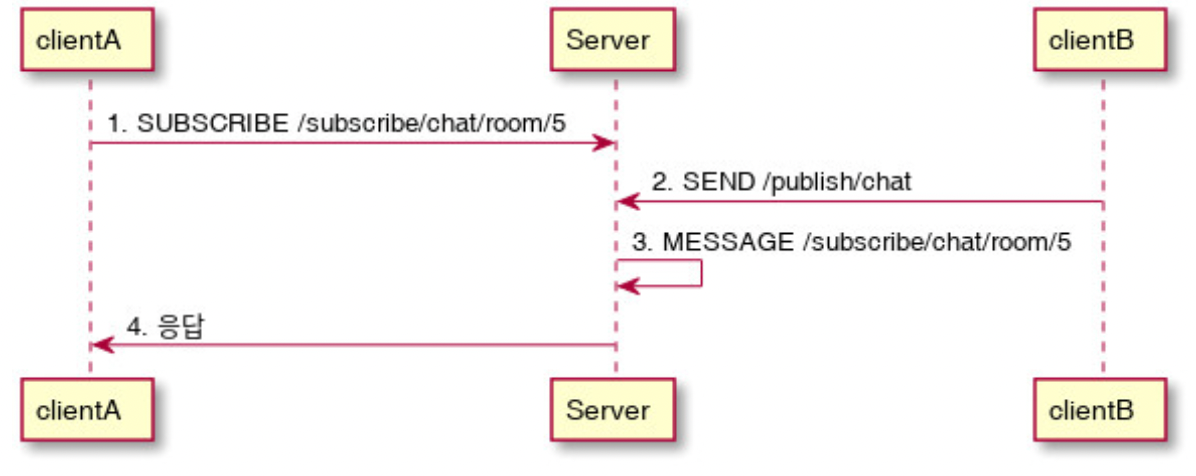


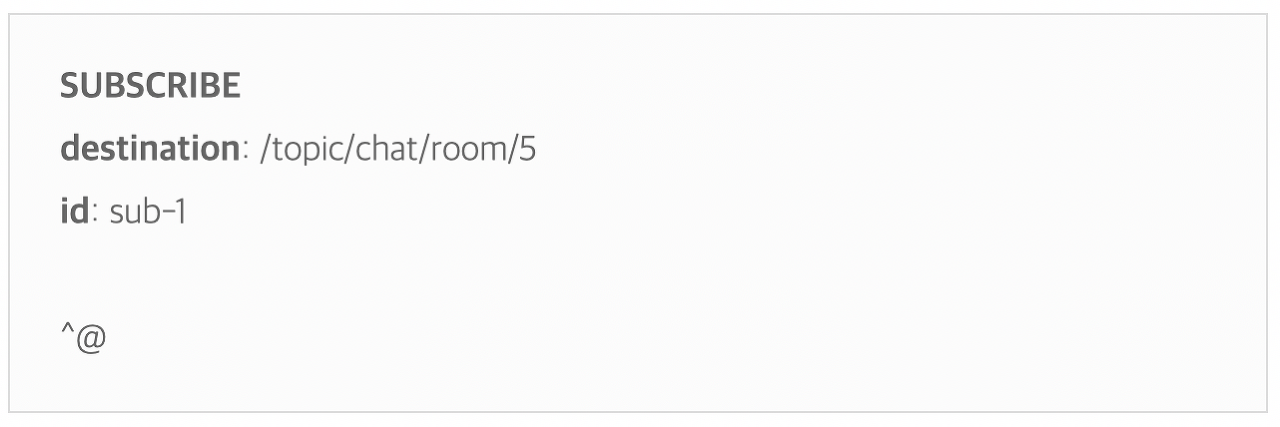


💡 Clients can use the SEND or SUBSCRIBE commands to send or subscribe for messages along with a "destination" header that describes what the message is about and who should receive it. This enables a simple publish-subscribe mechanism that can be used to send messages through the broker to other connected clients or to send messages to the server to request that some work be performed.
[문서해석]
클라이언트는 메세지의 내용과 누가 해당 메세지를 받을 것인가에 대한 정보를 알려주기 위해 SEND나 SUBSCRIBE 커맨드 사용이 가능하다. 이는 pub-sub 메커니즘을 사용하여 브로커를 통해 다른 클라이언트에게 메세지를 보내거나 수행되어야 할 기능들을 서버에 요청하기 위한 메세지 송신을 가능하게 한다.
💡 Publisher-Subscriber Model이란?

- Pub/Sub 구조는 비동기식(async) 메세징 패턴이다.
- Pub과 Sub은 메세지를 특정 수신자에게 다이렉트로 전달하는 시스템이 아니다. Pub은 메세지를 topic을 통해서 카테고리화하고 Sub은 그 topic을 구독함으로써 메세지를 읽어올 수 있다. Publisher은 topic에 대한 정보만 알고 있고, Sub도 topic만 바라보기 때문에 Pub과 Sub은 서로를 모르는 상태이다.
- Pub는 Sub에 대한 정보를 몰라도 일단 메세지를 Broker(Channel)에 보내놓는다. 이 때 메세지에 맞는 Topic으로 보내놓으면, 해당 Topic을 구독중인 Sub에게만 메세지가 가게 된다.
26.4.4 Flow of Messages
-default broker 사용
(RabbitMQ와 같이 external borker을 사용하는 케이스는 공식 문서 참고)

SimpleBroker은 SUBSCRIBE 중인 다른 클라이언트들에게 메세지를 보낸다. 또한 SimpleBroker은 클라이언트의 SUBSCRIBE 정보를 자체적으로 메모리에 유지한다.
- clientInboundChannel : WebSocket Client로부터 들어오는 요청을 전달하며, 클라이언트로부터 받은 메세지를 전달한다.
- clientOutboundChannel : WebSocket Client로 Server의 메세지를 내보내며, 클라이언트에게 메세지를 전달한다.
- brokerChannel : Server 내부에서 사용하는 채널이며, 이를 통해 SimpleAnnotationMethod는 SimpleBroker의 존재를 직접 알지 못해도 메세지를 전달할 수 있다. 서버의 어플리케이션 코드 내에서 broker에게 메세지를 전달한다.
- Message : headers와 payload를 포함하는 메세지의 표현
- MessageHandler : Message 처리에 대한 계약
- SimpleAnnotationMethod : @MessageMapping 등 Client의 SEND를 받아서 처리한다.
- SimpleBroker : Client의 정보를 메모리 상에 들고 있으며, Client로 메세지를 보낸다.
[과정]

@Configuration
@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerStompEndpoints(StompEndpointRegistry registry) {
registry.addEndpoint("/portfolio").withSockJs();
}
@Override
public void configureMessageBroker(MessageBrokerRegistry registry) {
registry.setApplicationDestinationPrefixes("/app"); *//For convenience, will use "/pub" later*
registry.enableSimpleBroker("/topic"); *//For convenience, will use "/sub" later*
}
}
@Controller
public class GreetingController {
//same as "/pub/greeting"
@MessageMapping("/greeting") {
public String handle(String greeting) {
return "[" + getTimestamp() + ": " + greeting;
}
}
💡 “/portfolio” is the HTTP URL for the endpoint to which a WebSocket (or SockJS) client will need to connect to for the WebSocket handshake. STOMP messages whose destination header begins with “/app”are routed to @MessageMapping methods in @Controller classes. Use the built-in, message broker for subscriptions and broadcasting; Route messages whose destination header begins with "/topic" or "/queue" to the broker.
[문서 해석]
“/portfolio”는 websocket과의 handshake을 위해 연결되어야 할 endpoint를 의미한다. “/app”으로 destination 헤더가 시작되는 STOMP 메세지들은 컨트롤러에서 @MessageMapping(SEND)로 경로한다. “/topic” 이나 “/queue”로 destination 헤더가 시작되면 브로커로 바로 향하게 된다(SUBSCRIBE).
- client가 “http://localhost:8080/portfolio”로 연결을 시도하고 webSocket 연결이 성공하면, STOMP frame이 작동되기 시작한다.
- 클라이언트가 SUBSCRIBE command를 “/topic/greeting” 이라는 destination 헤더를 보내면 우선 STOMP frame으로 decoding된다. decoding된 내용은 Spring 메세지 형태로 전환되며 이후 “clientInboundChannel”로 보내져 클라이언트의 구독 정보를 저장하고 있는 message broker로 라우팅된다.
- 클라이언트는 SEND command를 “/app/greeting”으로 보낸다. “/app” prefix는 어노테이트 된 컨트롤러로 라우팅 될 수 있게 해준다. 이후 “/app” prefix는 잘려지고, 남은 “/greeting” 부분은 컨트롤러에 있는 @MessageMapping와 매핑된다.(걍 pub으로 요청되었다가 나갈 때는 sub 붙여서 나가는거임). STOMP가 핸들러의 역할을 대신 해주므로 핸들러는 없어도 된다.
- 컨트롤러에서 반환된 값은 payload와 default destination headerd인 “/topic/greeting”을 담은 스프링 메세지로 전환된다. (prefix였던 “/app”은 잘려나가고 “/topic”으로 대체되어 default destination headerd인 “/topic/greeting”이 된다.)
- 메세지는 brokerChannel로 보내지고 이후 message broker에 의해 핸들된다.
- *message broker은 반환된 값과 일치하는 모든 구독자들을 찾아 **“clientOutboundChannel”*을 통해 MESSAGE command를 보낸다. 여기서 “clientOutboundChannel”은 메세지가 STOMP frame으로 다시 인코딩되어 WebSocket 연결쪽에 보내는 역할을 한다.
26.4.5 Annotated Controllers
- @MessageMapping : 목적지로 메세지를 라우팅해준다. @MessageMapping은 다양한 signatures(서명)을 갖을 수 있는데 자세한 내용은 공식문서를 참고하기로 하자. @MessageMapping 메소드에서 리턴된 값은 MessageConverter를 통해 payload로 serialized 되고, 이후 “brokerChannel”에 message가 보내지게 된다.
- @SubscribeMapping : @MesageMapping이 destination을 특정하는 반면 @SubscribeMapping은 메세지 정보만 포함하고 있다. 이 annotation을 사용하게 되면 컨트롤러의 리턴 값이 “brokerChannel”이 아닌 “clientOutboundChannel”로 보내지게 된다. 따라서 broker을 통해서 broadcasting이 되는 것이 아닌, 클라이언트에게 직접적으로 메세지가 전달되게 된다. 이는 request-reply가 one-off로 끝날 때 사용하기 유용하다.
- @MessageExceptionHandler : 컨트롤러에 해당 핸들러를 적용할 수 있다. 이를 더 전역적으로 관리하고 싶다면 @ControllerAdvice를 선언하여 사용하자.</aside>클라이언트는 메세지의 내용과 누가 해당 메세지를 받을 것인가에 대한 정보를 알려주기 위해 SEND나 SUBSCRIBE 커맨드 사용이 가능하다. 이는 pub-sub 메커니즘을 사용하여 브로커를 통해 다른 클라이언트에게 메세지를 보내거나 수행되어야 할 기능들을 서버에 요청하기 위한 메세지 송신을 가능하게 한다.
'항해 99(9기) > 항해 일일' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 항해 99 42일 차 (0) | 2022.10.31 |
|---|---|
| 항해 99 38일차 (1) | 2022.10.27 |
| 항해 99 37일차 (0) | 2022.10.26 |
| 항해 99 36일차 (0) | 2022.10.25 |
| 항해 99 35일차 (0) | 2022.10.24 |